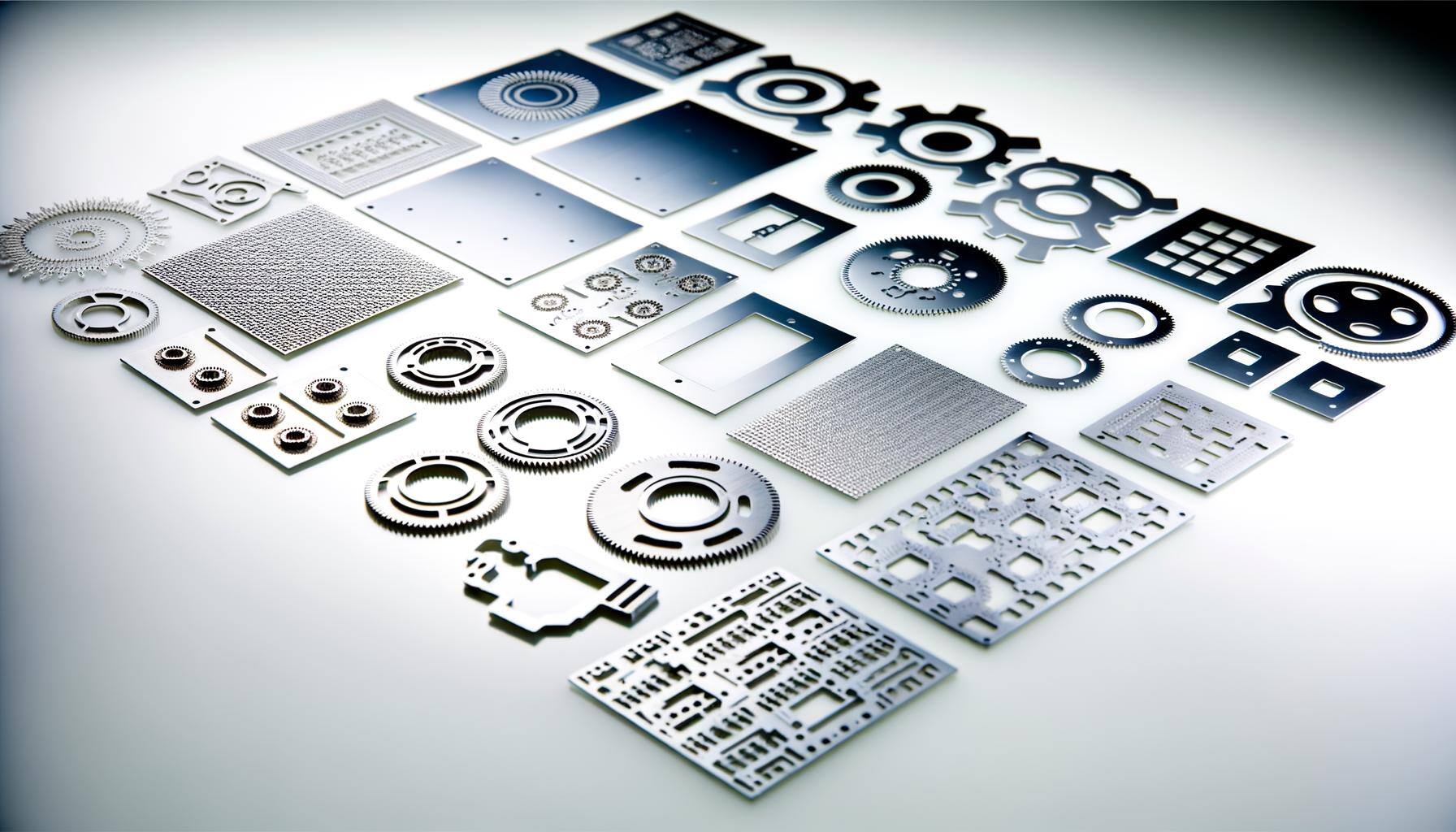
Industrial Applications of Photo Etching Across Sectors
Discover the transformative power of photo etching, a versatile and precise manufacturing process revolutionizing various industries.
The Fundamentals of Photo Etching
Photo etching, also known as chemical etching and photo chemical machining, is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses chemical solutions to remove material from a metal surface. This technique is highly precise and can create intricate and complex designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional machining methods.
To people familiar with printed circuit board fabrication, photo etching uses many of the same process steps: laminating, imaging and developing the photoresist, etching the metal and removing the resist. The key difference is that there is no non-conductive component such as Kapton for flex circuits or FR4 for rigid boards supporting the metal.
Designing for Photo Chemical Machining
Most of the "heavy lifting " in design these days is done by any of the solid modeling systems now in wide use. Most modern systems have design rules for different fabricating processes "baked into" the systems' architecture.
Unfortunately, none of them recognize photo chemical machining as a production option. So how can an engineer or designer compare whether stamping, laser cutting or photo etching would be the most effective and economical choice for manufacturing?
Rules for Efficiency and Economy
Choose An Alloy that's Available
The first step is to assess the application and try to select the most readily available types of metal alloys. All to often, we see projects where the specifier didn't take the time to research whether the selected alloy is actually available. Global events like the Covid pandemic and the "Great Recession" of 2008, roiled many industries, including the metal mills. As existing inventories were exhausted, the mills become much more selective about what they would manufacture. The "cornucopia" approach of make everything and eventually we'll sell it was replaced by only make what sells best. The mills aren't going to roll 50,000 pounds of something that is going to take 20 years to sell through any more.
Choose the Lightest Gauge that Satisfies the Application
It seems there may be a universal compulsion to enhance: if "A" is good, then "A-plus" must be better. Acquiescing to this compulsion in design for etching has three meaningful consequences:
- the metal weighs and therefore costs more ,
- the etching time -the most expensive time in the shop- increases in a linear fashion with the metal thickness, and
- the minimum dimensional tolerances, which are a function of metal thickness, range higher
Choose the Most Generous Tolerances Possible
While metal thickness defines what the minimum tolerances can be, more generous tolerances enable using largest possible sheet sizes for the best economy.
Diverse Industrial Applications of Photo Etching
Photo etching is employed across a broad range of industries due to its versatility and precision. In the electronics industry, it is used to manufacture components such as lead frames, RF shields, and connectors. The medical industry utilizes photo etching to produce surgical instruments, implantable devices, and microfluidic channels.
Metal filtration and other perforated products, including screens, masks, and grids and the like, are excellent candidates for photo etching. As are seals, gaskets, shims and other metal-to-metal applications.
In the aerospace and automotive sectors, photo etching is used to create intricate parts like fuel injector nozzles, filters, and heat exchangers. A significant move to using etched braze foil pre-forms has found many new applications in aerospace niches.
Fuels cells and batteries for mobile applications, including aircraft!, is a burgeoning area of growth for photo etching.
The process is also valuable in the production of decorative items, such as jewelry and nameplates, thanks to its ability to produce fine details and complex patterns.
Future Trends in Photo Etching Technology
The future of photo etching technology is promising, with ongoing advancements aimed at enhancing precision, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Innovations in photomask technology and photoresist materials are enabling higher resolution and more intricate designs.
Additionally, the development of eco-friendly etching solutions and waste treatment methods is addressing environmental concerns associated with chemical etching. As industries continue to demand smaller, more complex components, photo etching technology is poised to play a pivotal role in meeting these evolving needs.